CONTOUR SURVEY:
Contour line
The line of intersection of a level surface with the ground surface is known as the contour line or simply the contour. It can also be defined as a line passing through points of equal reduced levels.
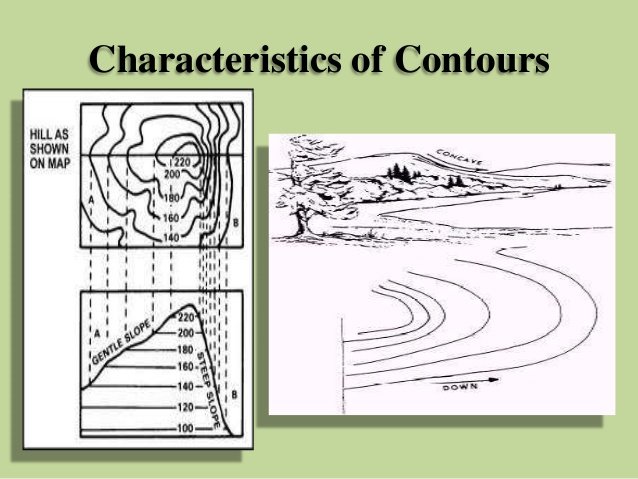
For example, a contour of 100 m indicates that all the points on this line have an RL of 100 m. Similarly, in a contour of 99 m, all points have an RL of 99 m, A map showing only the contour lines of an area is called a contour map.
Horizontal equivalent
The horizontal distance between any two consecutive contours is known as horizontal equivalent. It is not constant. It varies according to the steepness of the ground. For steep slopes, the contour lines run close together, and for flatter slope’s they are widely.
Object of Preparing Contour Map
The general map of a country includes the locations of roads, railways, rivers, villages, towns, and so on. But the nature of the ground surface cannot be realized, from such a map.
However, for all engineering projects involving roads, railways, and so on, knowledge of the nature of ground surface is required for locating suitable alignments and estimating the volume of earth work.
The process of tracing contour lines on the surface of earth is called contouring. A contour map gives the idea of the altitudes of the surface features as well as their relative positions in a plan.
Uses of Contour Maps
The following is the specific uses of the contour map:
- The nature of the ground surface of a country can be understood by studying a contour map. Hence, the possible route of communication between different places can be demarcated.
- A suitable, site or an economical alignment can be selected for any engineering project.
- The capacity of a reservoir or the area of a catchment can be approximately computed.
- The indivisibility or otherwise of different points can be established.
- A suitable route for a given gradient can be marked on the map.
- A section of the ground surface can be drawn in any direction from the contour map.

